Work-Bench enterprise report predicts end of SaaS could be coming
Work-Bench, a New York City venture capital firm that spends a lot of time around Fortune 1000 companies, has put together The Work-Bench Enterprise Almanac: 2018 Edition, which you could think of as a State of the Enterprise report. It’s somewhat like Mary Meeker’s Internet Trends report, but with a focus on the tools and technologies that will be having a major impact on the enterprise in the coming year.
Perhaps the biggest take-away from the report could be that the end of SaaS as we’ve known could be coming if modern tools make it easier for companies to build software themselves. More on this later.
While the report writers state that their findings are based at least partly on anecdotal evidence, it is clearly an educated set of observations and predictions related to the company’s work with enterprise startups and the large companies they tend to target.
As they wrote in their Medium post launching the report, “Our primary aim is to help founders see the forest from the trees. For Fortune 1000 executives and other players in the ecosystem, it will help cut through the noise and marketing hype to see what really matters.” Whether that’s the case will be in the eye of the reader, but it’s a comprehensive attempt to document the state of the enterprise as they see it, and there are not too many who have done that.
The big picture
The report points out the broader landscape in which enterprise companies — startups and established players alike — are operating today. You have traditional tech companies like Cisco and HP, the mega cloud companies like Amazon, Microsoft and Google, the Growth Guard with companies like Snowflake, DataDog and Sumo Logic and the New Guard, those early stage enterprise companies gunning for the more established players.

As the report states, the mega cloud players are having a huge impact on the industry by providing the infrastructure services for startups to launch and grow without worrying about building their own data centers or scaling to meet increasing demand as a company develops.
The mega clouders also scoop up a fair number of startups. Yet they don’t devote quite the level of revenue to M&A as you might think based on how acquisitive the likes of Salesforce, Microsoft and Oracle have tended to be over the years. In fact, in spite of all the action and multi-billion deals we’ve seen, Work-Bench sees room for even more.
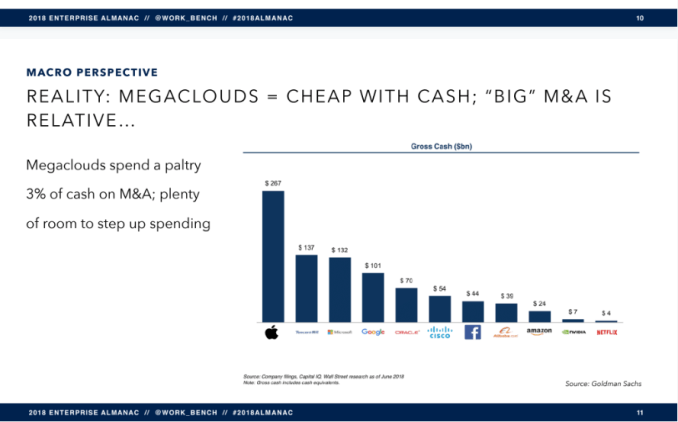
It’s worth pointing out that Work-Bench predicts Salesforce itself could become a target for mega cloud M&A action. They are predicting that either Amazon or Microsoft could buy the CRM giant. We saw such speculation several years ago and it turned out that Salesforce was too rich for even these company’s blood. While they may have more cash to spend, the price has probably only gone up as Salesforce acquires more and more companies and its revenue has surpassed $10 billion.
About those mega trends
The report dives into 4 main areas of coverage, none of which are likely to surprise you if you read about the enterprise regularly in this or other publications:
- Machine Learning
- Cloud
- Security
- SaaS
While all of these are really interconnected as SaaS is part of the cloud and all need security and will be (if they aren’t already) taking advantage of machine learning. Work-Bench is not seeing it in such simple terms, of course, diving into each area in detail.
The biggest take-away is perhaps that infrastructure could end up devouring SaaS in the long run. Software as a Service grew out of couple of earlier trends, the first being the rise of the Web as a way to deliver software, then the rise of mobile to move it beyond the desktop. The cloud-mobile connection is well documented and allowed companies like Uber and Airbnb, as just a couple of examples, to flourish by providing scalable infrastructure and a computer in our pockets to access their services whenever we needed them. These companies could never have existed without the combination of cloud-based infrastructure and mobile devices.
End of SaaS dominance?
But today, Work-Bench is saying that we are seeing some other trends that could be tipping the scales back to infrastructure. That includes containers and microservices, serverless, Database as a Service and React for building front ends. Work-Bench argues that if every company is truly a software company, these tools could make it easier for companies to build these kind of services cheaply and easily, and possibly bypass the SaaS vendors.

What’s more, they suggest that if these companies are doing mass customization to these services, then it might make more sense to build instead of buy, at least on one level. In the past, we have seen what happens when companies try to take these kinds of massive software projects on themselves and it hardly ever ended well. They were usually bulky, difficult to update and put the companies behind the curve competitively. Whether simplifying the entire developer tool kit would change that remains to be seen.
They don’t necessarily see companies running wholesale away from SaaS just yet to do this, but they do wonder if developers could push this trend inside of organizations as more tools appear on the landscape to make it easier to build your own.

The remainder of the report goes in depth into each of these trends, and this article just has scratched the surface of the information you’ll find there. The entire report is embedded below.
